Description
Product Description
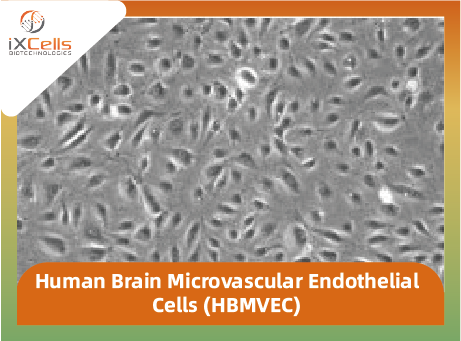
Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (HBMVEC) are the major element of the blood-brain barrier that shields the brain against toxins and immune cells via paracellular, transcellular, transporter, and extracellular matrix proteins [1]. HBMVEC are morphologically different from the peripheral endothelium. Brain endothelial cells lack fenestrations, have minimal pinocytic activity, are connected by tight junctions and have a large number of mitochondria associated with high metabolic activity [2]. Like peripheral endothelial cells, however, HBMVEC express, or can be induced to express, cell adhesion molecules on their surface that regulate the extravasation of leukocytes into the brain. HBMVEC have been widely used for studying the molecular and cellular function of blood-brain barrier [3].
iXCells Biotechnologies provides high quality HBMVEC, which are isolated from human brain and cryopreserved at P2, with ≥ 0.5 million cells in each vial. These HBMVEC express von Willebrand Factor (vWF), CD31 (PECAM), and Dil-Ac-LDL by uptake. They are negative for HIV-1, HBV, HCV, mycoplasma, bacteria, yeast, and fungi and can be further expanded for no more than 3 passages in Endothelial Cell Growth Media under the conditions suggested by iXCells Biotechnologies. Further expansion may decrease the purity.
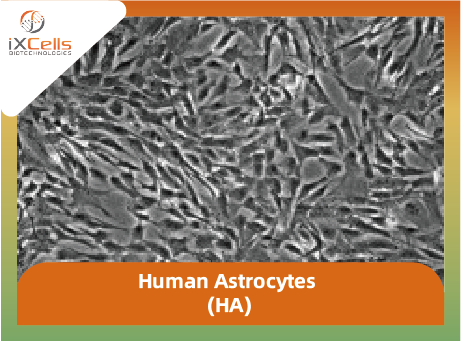
Figure 1. Human Brain Microvascular Endothelial Cells (HBMVEC). The cells were recovered, and seeded at 10,000 cells/cm2 following iXCells’ protocol. Phase contrast images were taken at the indicated time post recovery.
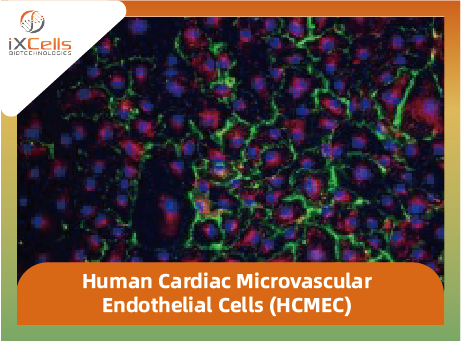
Figure 2. Immunofluorescence staining of HBMVEC with antibodies against CD31 (Green), VE-Cadherin (Red) and vWF (Green). Nuclei were counterstained by DAPI (Blue).
Product Details
| Organism | Homo Sapiens, Human |
| Cell Type | Endothelial Cell |
| Tissue | Human Brain |
| Disease | Normal |
| Package Size | 0.5 x 106 cells/vial |
| Passage Number | P2 |
| Growth Properties | Adherent |
| Product Format/Shipped | Cryopreserved |
| Storage | Liquid Nitrogen |
| Associated Media | Endothelial Cell Growth Media |
References
[1] Abbott, N. J., Patabendige, A. A., Dolman, D. E., Yusof, S. R., & Begley, D. J. (2010). Structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Neurobiology of disease, 37(1), 13–25.
[2] Yang, C., Hawkins, K. E., Doré, S., & Candelario-Jalil, E. (2019). Neuroinflammatory mechanisms of blood-brain barrier damage in ischemic stroke. American journal of physiology. Cell physiology, 316(2), C135–C153.
[3] Godinho-Pereira, J., Garcia, A. R., Figueira, I., Malhó, R., & Brito, M. A. (2021). Behind Brain Metastases Formation: Cellular and Molecular Alterations and Blood-Brain Barrier Disruption. International journal of molecular sciences, 22(13), 7057.




/HBMVEC-vWF%20and%20CD31.jpg)

Reviews
There are no reviews yet.