Description
***Temporarily on backorder due to high demand. Pre-order now or join the waitlist to be notified as soon as it’s available***
Product Description
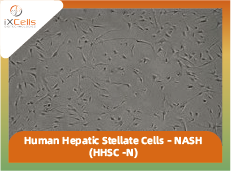
Hepatic stellate cells (HSCs) are liver-specific mesenchymal cells, and account for 5~8% of the cells in the liver. HSCs play vital roles in the homeostasis of liver extracellular matrix, repair, regeneration and fibrosis, and control retinol metabolism, storage and release. The stellate cell is the major cell type involved in liver fibrosis in response to liver injury.
In healthy liver, HSCs are in a quiescent state, and contains numerous vitamin A lipid droplets, constituting the largest reservoir of vitamin A in the body. When the liver is damaged, HSCs can change into an activated state, which is characterized by proliferation, contractility and chemotaxis. The amount of vitamin A decreases progressively in injured liver. The activated HSCs also secrete collagen scar tissue, which can lead to cirrhosis. In chronic liver disease, prolonged and repeated activation of stellate cells causes liver fibrosis [1,2].
In non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), hepatic stellate cells (HSC) differentiate into myofibroblast-like cells that cause fibrosis, which predisposes patients to cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Thus, modeling interactions between activated HSCs and hepatocytes in vitro can aid in the development of anti-NASH/fibrosis therapeutics and lead to a better understanding of disease progression [3].
iXCells Biotechnologies provides high quality Human Hepatic Stellate Cells – Nash (HHSC -N), which are isolated from liver tissue of NASH patient, and cryopreserved with >1 million cells in each vial. Each vial is sufficient to seed on four 10 cm dishes, and cells will be ready in 5~6 days to be passaged at 1:3 ratio. HHSC express Desmin and GFAP, and are negative for HIV-1, HBV, HCV, mycoplasma, bacteria, yeast, and fung. HHSC can further expand for 2-3 population doublings in Stellate Cell Growth Medium (Cat# MD-0014) under the condition suggested by iXCells Biotechnologies.
Product Details
| Tissue | Adult human liver from NASH patient |
| Package Size | 1.0 millioncells/vial |
| Shipped | Cryopreserved |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Growth Properties | Adherent |
| Media | Stellate Cell Growth Medium (Cat# MD-0014) |
References
[1] Chunyue Yin, et al, J Clin Invest. 2013;123(5):1902–1910. Hepatic stellate cells in liver development, regeneration, and cancer.
[2] Rockey D. C. . Semin Liver Dis 21(3):337-49. (2001) Hepatic blood flow regulation by stellate cells in normal and injured liver.
[3] Davidson MD. Integr Biol (Camb).9(8):662-677.( 2017)Microengineered cultures containing human hepatic stellate cells and hepatocytes for drug development.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.