Description
Product Description
The primary human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMEC), also termed as Human Lung Microvascular Endothelial Cells (HLMVEC), form a luminal barrier of intra-acinar arterioles that is critical for lung gas exchange and regulation of fluid and solute passage between the blood and interstitial compartments in the lung. They also have metabolic properties that enable it to carry out certain important nonrespiratory function [1]. The HPMEC are among the most important targets of reactive oxygen species elaborated in lung injury. During the lung inflammation, neurohumoral mediators and oxidants act on endothelial cells to induce intercellular gaps permissive for transudation of proteinaceous fluid from blood into the interstitium [2]. The increased permeability leads to the hypoxemia associated with adult respiratory distress syndrome and noncardiogenic pulmonary edema [3].
iXCells Biotechnologies provides high quality HPMEC, which are isolated from human lung tissue and cryopreserved at P2, with >0.5 million cells in each vial. HPMEC express vWF/Factor VIII, CD31 (PECAM), and Dil-Ac-LDL by uptake. They are negative for HIV-1, HBV, HCV, mycoplasma, bacteria, yeast, and fungi and can further expand no more than 3 passages in Endothelial Cell Growth Media under the condition suggested by iXCells Biotechnologies. Further expansion may decrease the purity.

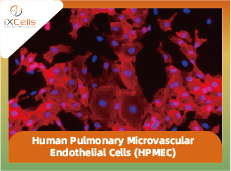
Figure 1. Human Pulmonary Microvascular Endothelial Cells (HPMVEC). (A) Phase contrast image of HPaMEC. (B & C) Immunofluorescence staining with antibodies against CD31 (B) and vWF/Factor VIII (C).
Product Details
| Tissue | Human lung tissue |
| Package Size | 0.5 millioncells/vial |
| Passage Number | P2 |
| Shipped | Cryopreserved |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Growth Properties | Adherent |
| Media | Endothelial Cell Growth Media |
References
[1] Brigham, K. L. (1990) Oxidant stress and adult respiratory distress syndrome. Eur Respir J Suppl 11: 482s-484s.
[2] Moore T. M., Chetham P. M., Kelly J. J., Stevens T. (1998) Signal transduction and regulation of lung endothelial cell permeability. Interaction between calcium and cAMP. Am J Physiol. 275(2 Pt 1):L203-22.
[3] Kelly JJ, Moore TM, Babal P, Diwan AH, Stevens T, Thompson WJ. (1998) Pulmonary microvascular and macrovascular endothelial cells: differential regulation of Ca2+ and permeability. Am J Physiol. 274(5 Pt 1):L810-9.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.