Description
Product Description
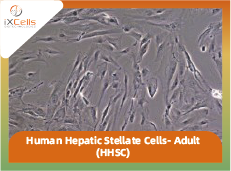
Hepatic stellate cells(HSC) are liver-specific mesenchymal cells, and account for 5~8% of the cells in the liver. HSC play vital roles in the homeostasis of liver extracellular matrix, repair, regeneration and fibrosis, and control retinol metabolism, storage, and release. Stellate cell is the major cell type involved in liver fibrosis in response to liver injury. In healthy liver, HSC are in a quiescent state, and contains numerous vitamin A lipid droplets, constituting the largest reservoir of vitamin A in the body. When the liver is damaged, HSC can change into an activated state, which is characterized by proliferation, contractility, and chemotaxis. The amount of vitamin A decreases progressively in injured liver. The activated HSC is also responsible for secreting collagen scar tissue, which can lead to cirrhosis. In chronic liver disease, prolonged and repeated activation of stellate cells causes liver fibrosis [1,2]. Primary culture of HSC is a valuable tool to study liver fibrosis.
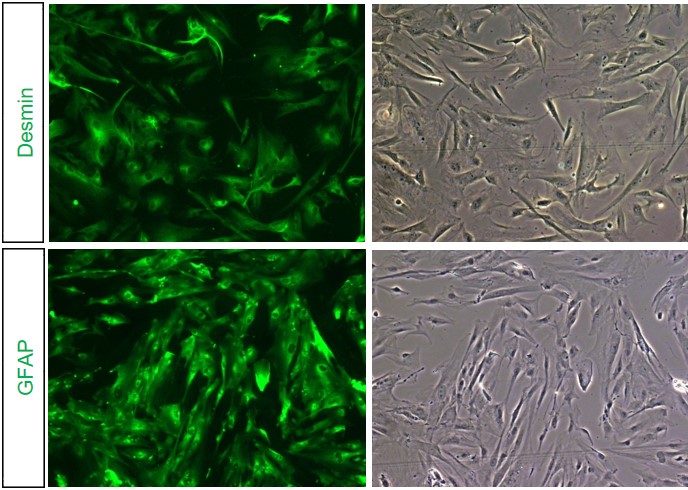
Human Hepatic Stellate Cells (HHSC) from iXCells Biotechnologies are isolated from adult human liver and cryopreserved with ≥ 1 million cells in each vial. HHSC are characterized by immunofluorescence with antibodies specific to Desmin and GFAP. They are negative for HIV-1, HBV, HCV, mycoplasma, bacteria, yeast, and fungi. HHSC can be further expanded for 2-3 passages in iXCells’ Stellate Cell Growth Medium (Cat# MD-0014).

Figure 1. Human hepatic stellate cells (HHSC) stained with Desmin and GFAP (green). Corresponding phase contrast images of each staining is shown to the right.
Product Details
| Tissue | Adult human liver |
| Package Size | 1.0 million cells/vial |
| Shipped | Cryopreserved |
| Storage | Liquid nitrogen |
| Growth Properties | Adherent |
| Media | Stellate Cell Growth Medium (Cat# MD-0014) |
References
[1] Yin, C., Evason, K. J., Asahina, K., & Stainier, D. Y. (2013). Hepatic stellate cells in liver development, regeneration, and cancer. The Journal of clinical investigation, 123(5), 1902–1910.
[2] Rockey D. C. (2001). Hepatic blood flow regulation by stellate cells in normal and injured liver. Seminars in liver disease, 21(3), 337–349.




Reviews
There are no reviews yet.